This site is made to provide information about recently started Pharm D and Pharm D(Post Bacclaurreatte) courses in india to all
Saturday, 30 August 2025
Phamacy Council Election
Monday, 18 August 2025
'Profession Vs Job' - Professional standards do not compromise whereas Job standards can be compromised.!
Thursday, 14 August 2025
Vision Of The Indian PPR Act by Bhagwan PS
Monday, 11 August 2025
PCI to integrate pharmacists' database with Healthcare Professional Registry
PCI to integrate pharmacists' database with Healthcare Professional Registry |
| Gireesh Babu, New Delhi Saturday, November 23, 2024, 08:00 Hrs [IST] |
Pharmacists are HealthCare Professionals. Lets be worth it. Really!!!, then why the term ' PharmaCare ' was coined. Pharmacist A HealthCare professional? If so why pharmacy course is not?. Has the Pharmacy education been got included in National Health Education Manual? |
So many regulatory bodies and governing bodies in pharmacy education: whims of my mind
Now with the advent of Pharm D course in pharmacy, which is clinically oriented 6 years course in pharmacy and the syllabus is designed such as first 3 years are same as B.Pharm ( compounding and dispensing oriented) and next 2 years are same as MD Pharmacology (medically and clinically oriented) and 1 year of internship in an attached (minimum- 300 beded) hospital , one may expect MCI (medical council of India) to get into the thick of the things/matters.
As it requires an affiliation with a hospital( minimum 300 beded), to get approval for an pharmaceutical institute from PCI to conduct the course , one must expect MCI(medical council of India)(Now NMC) also to get involved as a regulatory and governing body.
PCI governs courses like : D.Pharm
B.Pharm
Pharm D and Pharm D(PB)
AICTE governs courses like : B.Pharm( jointly with PCI)
M.Pharm
Now one must expect AICTE,PCI and MCI may jointly govern : Pharm D and Pharm D(PB)
But no, its not a rational thinking on my part. MCI (Now NMC ) will get involve only when the course is a medical one or may be when the professional doctor is dealing with a body part.
So, its fair enough that MCI(NMC) is not involved into these matters.(Really?!!!)
Pharm D course introduction and D Pharma course closure is Propaganda !!! Is Pharm D and Pharm D(PB) course is approved by UGC?
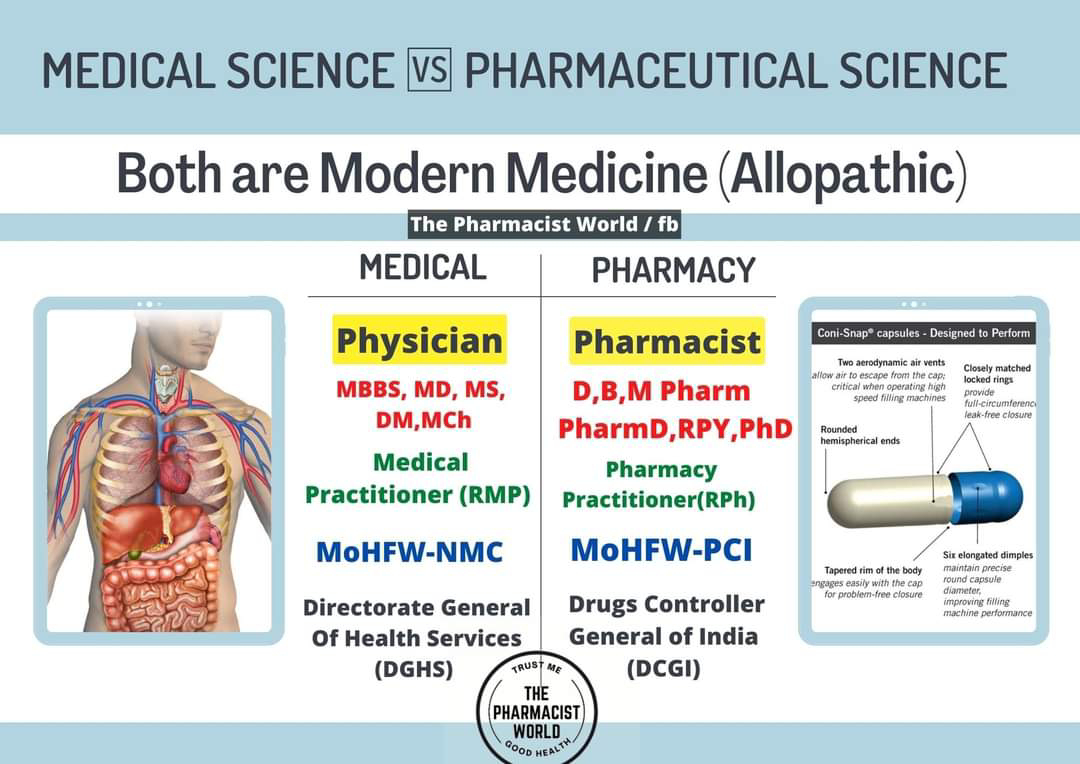
Medical Science vs Pharmaceutical Science (Residential Program Year)
- Pharm.D. as a Professional Qualification:The Pharm.D. is a professional doctorate recognized by the Pharmacy Council of India (PCI). It signifies expertise in pharmacy practice and allows graduates to become licensed pharmacists.
- Residency Programs:
- Following the Pharm.D., residency programs offer specialized training in various clinical settings, such as hospitals and clinics.
- Focus Areas:
- Residency programs can focus on areas like:
- Clinical Pharmacy: Providing patient-centered care, medication therapy management, and drug information services.
- Critical Care: Managing patients in intensive care units, focusing on advanced life support and critical care protocols.
- Other Specializations: Opportunities may also exist in areas like oncology, cardiology, and infectious disease, depending on the specific program and institution.
- Career Paths:
- Residency training can lead to various career opportunities, including:
- Clinical Pharmacist Roles: In hospitals and other healthcare settings, directly involved in patient care.
- Medical Affairs: Bridging the gap between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare professionals, providing scientific expertise and support.
- Research: Participating in clinical trials and research activities.
- Duration:Residency programs typically last one to two years, depending on the specialization and institution.
- Benefits:Residency programs offer valuable practical experience, enhance clinical skills, and improve career prospects for Pharm.D. graduates.
The term residency is named as such due to resident physicians (resident doctors) of the 19th century residing at the dormitories of the hospital in which they received training.[1]
In many jurisdictions, successful completion of such training is a requirement in order to obtain an unrestricted license to practice medicine, and in particular a license to practice a chosen specialty. In the meantime, they practice "on" the license of their supervising physician. An individual engaged in such training may be referred to as a resident physician, house officer, registrar or trainee depending on the jurisdiction. Residency training may be followed by fellowship or sub-specialty training.[2]
Whereas medical school teaches physicians a broad range of medical knowledge, basic clinical skills, and supervised experience practicing medicine in a variety of fields, medical residency gives in-depth training within a specific branch of medicine.
- Duration: Generally 3 years for most specialties, but can vary.
- Eligibility: Requires completion of MBBS and passing the NEET-PG exam.
- Structure: Includes clinical rotations, academic learning (case discussions, seminars, etc.), and research.
- Focus: Hands-on clinical experience and development of practical skills under supervision.
- Outcome: Leads to an MD or MS degree in the chosen specialty and prepares doctors for independent practice.
- Supervision: Residents work under the guidance of attending physicians and consultants.
- Workload: Residents typically work long hours, including nights, weekends, and holidays.
 The Pharmacy Council of India (PCI) has sought all the pharmacists who don't have the ABHA (Ayushman Bharat Health Account) number to attain a number and ensure registration with the DIGI-PHARMed profile with the ABHA number on immediate basis, as part of its efforts to integrate the pharmacists' list with the Healthcare Professional Registry (HPR).
The Pharmacy Council of India (PCI) has sought all the pharmacists who don't have the ABHA (Ayushman Bharat Health Account) number to attain a number and ensure registration with the DIGI-PHARMed profile with the ABHA number on immediate basis, as part of its efforts to integrate the pharmacists' list with the Healthcare Professional Registry (HPR).